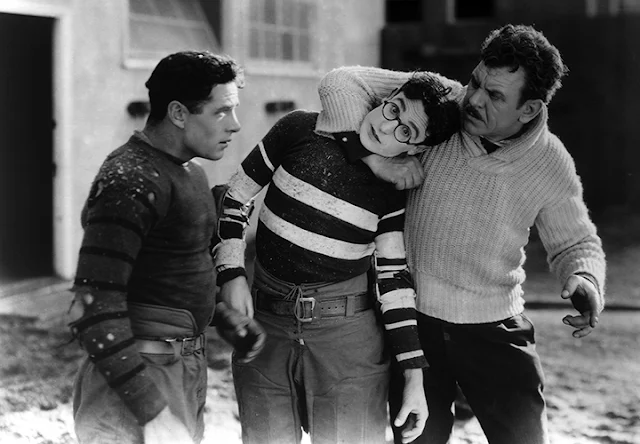
Cast: Harold Lloyd, Jobyna Ralston, Brooks Benedict, James H. Anderson, Hazel Keener, Joseph Harrington, Pat Harmon. Screenplay: Sam Taylor, Ted Wilde, John Gray, Tim Whelan; titles: Thomas J. Gray. Cinematography: Walter Lundin. Art direction: Liell K. Vedder. Film editing: Allen McNeil.
Wouldn't it be great if all silent films could be as lovingly restored as Harold Lloyd's The Freshman has been? Though not as excitingly hilarious as his Safety Last! (Fred C. Newmeyer and Sam Taylor, 1923), this is probably Lloyd's most polished feature, a good-natured take on the mythos of American college football. It was made in an era when the word "college" meant raccoon coats and hip flasks at places like "Tate University -- a large football stadium, with a college attached," as the intertitle sardonically puts it. The era came to an end with World War II and the consequent GI Bill, which democratized higher education -- and also turned college football into the pseudo-professional sport that it is today. This was an era in which the myth of the gridiron hero could still inspire a schlub like Lloyd's Harold Lamb, infatuated with the idea of becoming a big man on campus. Tellingly, it's a movie that gives Lamb the idea and the mannerisms he naively takes with him as he matriculates at Tate. The Freshman is essentially a send-up of the movie-made myth, cheerfully furthering the myth with Lamb's own unlikely heroism.